A bone marrow transplant involves transplanting blood cells, which move to the bone marrow to further produce new blood cells and promote the growth of new marrow.
A bone marrow transplant involves transplanting blood cells, which move to the bone marrow to further produce new blood cells and promote the growth of new marrow. It is a medical procedures performed by transplanting blood cells, i.e. replacing the destroyed and damaged cells with the healthy cells to help your body make enough platelets, white blood cells, or red blood cells to avoid infections, bleeding disorders, or anemia. In a bone marrow transplant, procedure the bone marrow that has been damaged or destroyed is replaced by disease, infection. This procedure
This procedure of bone marrow is usually performed when the patients are suffering from conditions like a plastic anemia, leukemia, Hodgkin’s lymphoma, or thalassemia major.
Usually, doctors recommend one of the following three types of bone marrow transplantations –
Before a bone marrow transplant procedure, the Doctor will recommend a few tests to discover what type of bone marrow cells patient needs. The patient might also undergo radiation to kill off all cancer cells or marrow cells before getting the new cells. Before your treatment, the health care team will explain the patient about the transplant process and answer all the questions. The pre-transplant period is characterized by the identification of the appropriate type of transplant that will be done and, if necessary, finding an appropriate donor for the transplant.
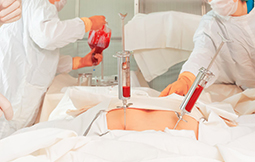
During the procedure of bone marrow transplant the patient is given general anesthesia before performing the actual treatment to allow the surgeon to easily and painlessly extract the cells by inserting needles in the region around his or her pelvic bone. The surgeon will then tests the cells to make sure they are clean and healthy, after which they are preserved until the scheduled transplant.
When the patient is ready for the transplant. The procedure for transplanting the healthy cells is performed which is similar to a blood transfusion. If the patient has an allogeneic transplant, bone marrow cells will be harvested from the donor a day or two before the procedure. If the patient’s own cells will be used, they’ll be retrieved from the cell bank.
Cells are collected in two ways:
During a bone marrow harvest, cells will be collected from both hipbones through a needle. The patient will be given anesthesia for this procedure, meaning that the patient will be asleep and free of any pain.
The entire BMT procedure takes around 3 to 4 hours from the time the cells enter the body and reach and bone marrow to start producing healthy cells. This process is called engraftment.
The success rate of a bone marrow transplant generally depends on how closely the donor and recipient genetically match and in some cases; it can be very difficult to find a good match among unrelated donors. After completion of the procedure the state of engraftment will be regularly monitored by the doctor. It generally takes between 10 and 28 days to finish after the initial transplant. The very first sign of engraftment is a rising white blood cell count. This will let help the patient to know that the transplant is starting to make new blood cells. Typical recovery time for this treatment is about three months. However, it may take about a year for you to recover fully.
There are fewer risks associated with this treatment because only a small amount of the bone marrow is removed from the body. The usual symptoms that the patient may experience after the treatment might include stiffness, slight pain, and weakness for a few days.
Complications might be mild or very serious. The major complications that are associated with the treatment may include:
In some of the many cases, graft-versus-host diseases can become a long-lasting condition. In this case, you may get –
Copyright © 2025 IMA | All Rights Reserved.