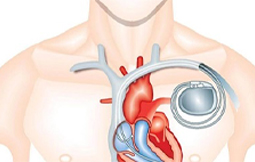
A pacemaker is a little device that’s placed under the skin in your chest to help regulate your heartbeat. It’s used to help your heart beat more regularly if you have an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia), especially a slow one.
A pacemaker is a little device that’s placed under the skin in your chest to help regulate your heartbeat. It’s used to help your heart beat more regularly if you have an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia), especially a slow one. Implanting a pacemaker in your chest needs a surgical procedure.
Pacemakers are implanted to help control your heartbeat. They can be inserted temporarily to treat a slow heartbeat after a heart attack, surgery, or medication overdose. Or they can be implanted permanently to fix a slow or irregular heartbeat or, in some people, to help treat heart failure.
You’ll likely be awake throughout the surgery to implant the pacemaker, which typically takes a few hours. You’ll have an intravenous line placed, through which you might receive medication to help you relax. Most pacemaker implantations are done using local anesthesia to numb the area of incisions. Your chest is cleaned with a special soap.
One or more flexible, insulated wires are inserted into a major vein under or near your collarbone and guided to your heart using X-ray images. One end of each wire is secured to the proper position in your heart, while the other end is attached to the pulse generator, which is usually implanted under the skin beneath your collarbone.
You’ll likely wait in the hospital for a day after having a pacemaker implanted. Your pacemaker will be programmed to suit your pacing needs. Arrange to have someone drive you home when you’re discharged. Most pacemakers can be checked remotely. Your pacemaker transmits to and receives information from your doctor’s office, including your heart rate and rhythm, how your pacemaker is working, and its remaining battery life. Your doctor might recommend that you avoid vigorous exercise or heavy lifting for about a month. Avoid putting pressure on the area where the pacemaker was implanted. If you have pain in that area, ask your doctor about taking over-the-counter medicines, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others).
Copyright © 2025 IMA | All Rights Reserved.